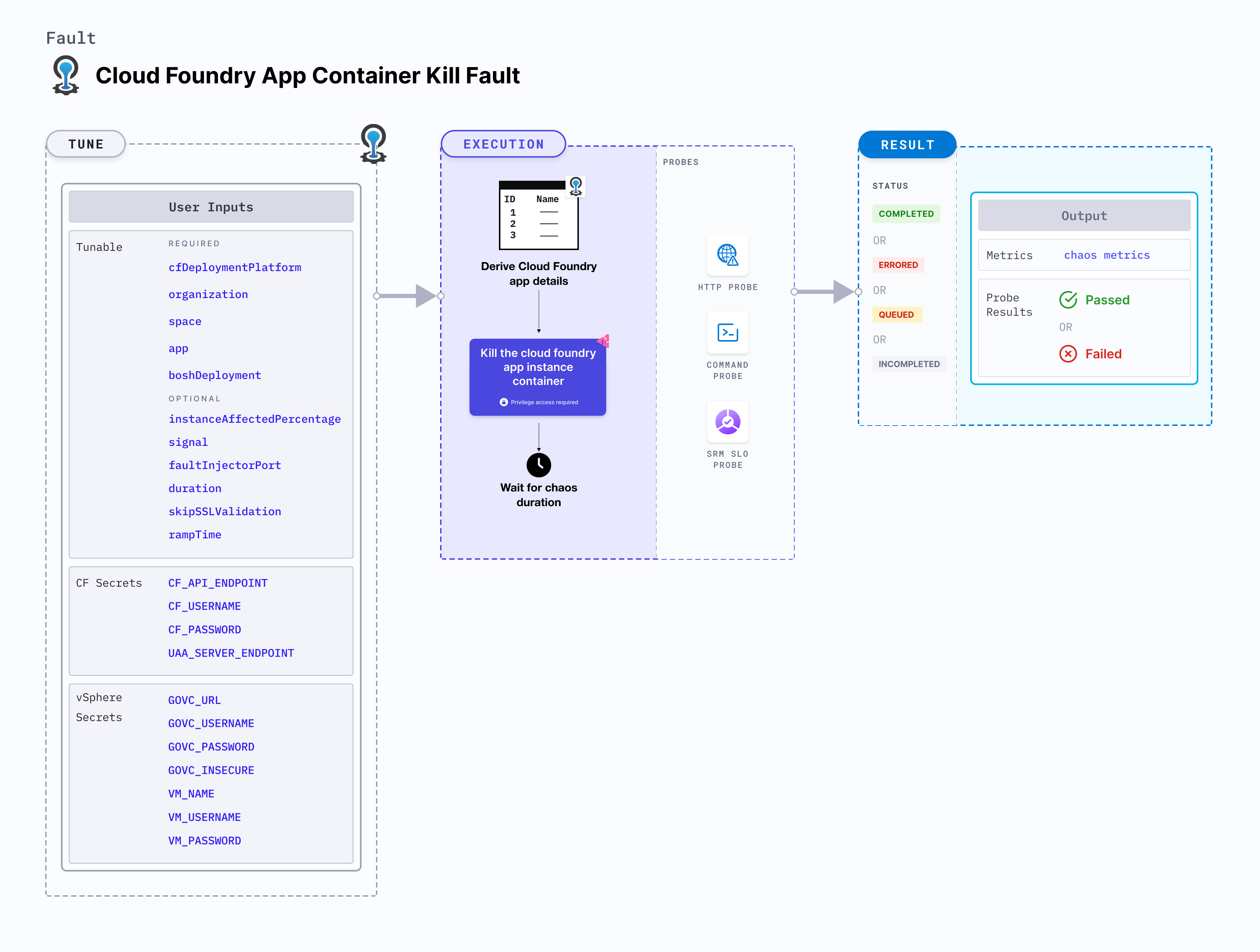
CF app container kill
CF app container kill causes a Cloud Foundry app instance container to be killed (crash) and restarted.
Use cases
CF app container kill:
- Checks resilience upon app instance crash due to container unavailability.
- Validates the effectiveness of disaster recovery and high availability of the app.
Mandatory tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| deploymentModel | The deployment model being used for Linux Chaos Infrastructure + Cloud Foundry Fault Injector. For more information, refer here. | One of: model-1,model-2. No default value is assumed, if the tunable is not provided. For model-1, boshDeployment and faultInjectorLocation inputs are not required. |
| organization | Organization where the target app resides. | For example, dev-org |
| space | Space where the target app resides. | The space must reside within the given organization. For example, dev-space |
| app | The app to be stopped. | The app must reside within the given organization and space. For example, cf-app |
Optional tunables
| Tunable | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| faultInjectorLocation | Fault injector placement with respect to where the LCI is hosted. | Default: local. Supports local and vSphere. For more information, go to Fault Injector location. |
| boshDeployment | The bosh deployment under which the CF components are being managed. | It can be obtained using the BOSH CLI command bosh deployments. For more information, go to BOSH deployment. |
| instanceAffectedPercentage | Percentage of total number of app instances that will be targeted. | Default: 0 (1 instance). For more information, go to instance affected percentage. |
| signal | The signal to send while killing the container. Supports both names and corresponding numbers to denote a signal. | Default: SIGKILL. For more information, go to signal. |
| faultInjectorPort | Local server port used by the fault-injector utility. | Default: 50320. If the default port is unavailable, a random port in the range of 50320-51320 is selected. For more information, go to fault injector port. |
| duration | Duration through which chaos is injected into the target resource (in seconds). | Default: 30s. For more information, go to chaos duration. |
| skipSSLValidation | Skip SSL validation while invoking CF APIs. | Supports true and false. Default: false. For more information, go to skip SSL validation. |
| rampTime | Period to wait before and after injecting chaos (in seconds). | Defaults to 0. |
CF secrets
The following Cloud Foundry secrets reside on the same machine where the chaos infrastructure is executed. These secrets are provided in the /etc/linux-chaos-infrastructure/cf.env file in the following format:
CF_API_ENDPOINT=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
CF_USERNAME=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
CF_PASSWORD=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
UAA_SERVER_ENDPOINT=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
BOSH_CLIENT=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
BOSH_CLIENT_SECRET=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
BOSH_CA_CERT=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
BOSH_ENVIRONMENT=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
If the secrets file is not provided, the secrets are attempted to be derived from environment variables and the config file by the fault-injector.
| ENV name | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| CF_API_ENDPOINT | API endpoint for the CF setup | https://api.system.cf-setup.com |
| CF_USERNAME | Username for the CF user | username |
| CF_PASSWORD | Password for the CF user | password |
| UAA_SERVER_ENDPOINT | API endpoint for the UAA server for the CF setup | https://uaa.system.cf-setup.com |
| BOSH_CLIENT | Used by the bosh CLI, the BOSH client | admin |
| BOSH_CLIENT_SECRET | Used by the bosh CLI, the BOSH client secret | UBu9Fu3oW35sO6fw12auPH76gsRTy7 |
| BOSH_CA_CERT | Used by the bosh CLI, the file path for BOSH CA certificate | /root/root_ca_certificate |
| BOSH_ENVIRONMENT | Used by the bosh CLI, the BOSH environment | bosh.corp.local |
Fault injector ENVs and config file
If /etc/linux-chaos-infrastructure/cf.env file is not provided, fault-injector attempts to derive the secrets from environment variables or a configuration file. Any secret that is re-declared will be overridden in the following order of decreasing precedence:
/etc/linux-chaos-infrastructure/cf.envfile- Environment variables
- Configuration file
The configuration file should be provided at /etc/linux-chaos-infrastructure/cf-fault-injector.yaml:
cf-api-endpoint: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
username: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
password: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
uaa-server-endpoint: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
bosh-client: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
bosh-client-secret: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
bosh-ca-cert: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
bosh-environment: XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
A mapping between all the three formats for providing the secrets is as follows:
| cf.env | ENV | cf-fault-injector.yaml |
|---|---|---|
| CF_API_ENDPOINT | CF_API_ENDPOINT | cf-api-endpoint |
| CF_USERNAME | USERNAME | username |
| CF_PASSWORD | PASSWORD | password |
| UAA_SERVER_ENDPOINT | UAA_SERVER_ENDPOINT | uaa-server-endpoint |
| BOSH_CLIENT | BOSH_CLIENT | bosh-client |
| BOSH_CLIENT_SECRET | BOSH_CLIENT_SECRET | bosh-client-secret |
| BOSH_CA_CERT | BOSH_CA_CERT | bosh-ca-cert |
| BOSH_ENVIRONMENT | BOSH_ENVIRONMENT | bosh-environment |
vSphere secrets
These secrets are provided only if vSphere is used as the deployment platform for CF.
The following vSphere secrets reside on the same machine where the chaos infrastructure is executed. These secrets are provided in the /etc/linux-chaos-infrastructure/vsphere.env file in the following format:
GOVC_URL=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
GOVC_USERNAME=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
GOVC_PASSWORD=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
GOVC_INSECURE=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
VM_NAME=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
VM_USERNAME=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
VM_PASSWORD=XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX
| ENV Name | Description | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| GOVC_URL | Endpoint for vSphere | For example, 192.168.214.244 |
| GOVC_USERNAME | Username for the vSphere user | For example, username |
| GOVC_PASSWORD | Password for the vSphere user | For example, password |
| GOVC_INSECURE | Skip SSL validation for govc commands | For example, true |
| VM_NAME | Name of the vSphere VM where the fault-injector utility is installed | For example, cf-vm |
| VM_USERNAME | Username for the VM guest user | For example, root |
| VM_PASSWORD | Password for the VM guest user | For example, password |
Fault Permissions
List all applications the user or client has access to
Required Roles (any one):
SpaceDeveloper(in the app’s space)SpaceAuditor(read-only role in the app’s space)OrgManagerorOrgAuditor(at the org level)
Required OAuth Scopes (for tokens):
cloud_controller.readcloud_controller.admincloud_controller.global_auditor
List all BOSH deployments
Required Role:
- BOSH user with read permissions (typically
adminor a user withreadaccess to deployments)
Required Auth:
- Valid BOSH UAA token with
bosh.readscope
Establish SSH session to a Diego Cell via BOSH SSH
Required Role:
- BOSH user with SSH access permissions for the Diego Cell instance group
Required Auth:
- BOSH UAA token with
bosh.sshorbosh.adminscope
Use cfdot to list LRPs and locate app containers
Required Role:
- Operator with SSH access to a cell and executable access to
cfdot
Required Auth:
- Requires
diego.readscope in BOSH UAA or access to the Diego BBS with a trusted client certificate
Use ctr to get container-level metadata and target container PIDs
Required Role:
- SSH-level access to the cell host and root access (or
sudo) to interact with containerd
Required Auth:
- None via API; requires root or elevated access on the host to inspect or query containerd
Kill the target container using ctr
Required Role:
- Root access on the Diego Cell to execute
ctr tasks killor equivalent containerd lifecycle commands
Required Auth:
- None via API; kill is performed via local host access and requires system-level privileges
Signal
The signal input determines the signal to be sent while killing the container.
- It defaults to
SIGKILL. - It can be specified using the name (eg.
SIGKILL) or the corresponding integer (eg.9).
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# app container kill signal
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: vSphere
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
boshDeployment: cf
signal: "15"
Deployment Model
The deploymentModel input specifies the LCI deployment model with respect to its placement in the host TAS VM.
- It accepts one of:
model-1,model-2. - No default value is assumed if the input is not provided, but the experiment execution fails with an error.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# deployment model for LCI
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: vSphere
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
boshDeployment: cf
deploymentModel: model-1
BOSH deployment
The boshDeployment input determines the BOSH deployment name under which all the CF resources are being managed. It can be obtained using the BOSH CLI command bosh deployments.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# bosh deployment
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: vSphere
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
boshDeployment: cf
Instance affected percentage
The instanceAffectedPercentage input specifies the percentage of total number of app instances that will be targeted. It defaults to 0 (1 instance).
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# instance affected percentage
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: vSphere
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
boshDeployment: cf
instanceAffectedPercentage: 50
Fault Injector location
The faultInjectorLocation input determines the fault injector placement with respect to where the LCI is hosted.
- It supports one of:
local: LCI and fault injector are placed in the same machine.vSphere: Fault injector is placed in a remote vSphere managed VM.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# Fault Injector location
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: vSphere
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
Skip SSL validation
The skipSSLValidation input variable determines whether to skip SSL validation for calling the CF APIs.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# skip ssl validation for cf
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: vSphere
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
skipSSLValidation: true
Fault injector port
The faultInjectorPort input variable determines the port used for the fault-injector local server.
The following YAML snippet illustrates the use of this environment variable:
# fault injector port
apiVersion: litmuchaos.io/v1alpha1
kind: LinuxFault
metadata:
name: cf-app-container-kill
labels:
name: app-container-kill
spec:
cfAppContainerKill/inputs:
duration: 30s
faultInjectorLocation: local
app: cf-app
organization: dev-org
space: dev-space
faultInjectorPort: 50331